
The light incident at an angle greater than critical angle will The light that is incident on the water surface atĪn angle less than the critical angle will undergo refraction and emerge outįrom the water. Radius of illumination (Snell’s window)īulb is kept inside a water tank, the light from the source travels in allĭirection inside the water. Prisms are also used to invert images withoutĬhanging their size as shown in Figure. We see from Table 6.3 that this is true for bothĬrown glass and flint glass. In the first two cases, the critical angle i cfor the material of the Light by 90º or by 180º by making use of total internal reflection as shown inįigure 6.24(a) and (b). Hence, an inverted image is formed littleĪbove the surface as shown in Figure 6.23(b). In the cold regions like glaciers and frozen lakes and seas, the

Thus, theĭensity and refractive index of air near the ground is greater than at a Ground is lesser than the temperature above the surface of earth. Index increases towards the ground because the temperature of air close to the Of the layers of air, the observer feels as if the object is getting reflectedīy a pool of water or wet surface beneath the object as shown in FigureĦ.23(a). This gives an illusionĪs if the light comes from somewhere below the ground. Of incidence near the ground exceeds the critical angle. Hence, a ray of light successively deviates away from the normal atĭifferent layers of air and undergoes total internal reflection when the angle Like a tree, passes through a medium whose refractive index decreases towards
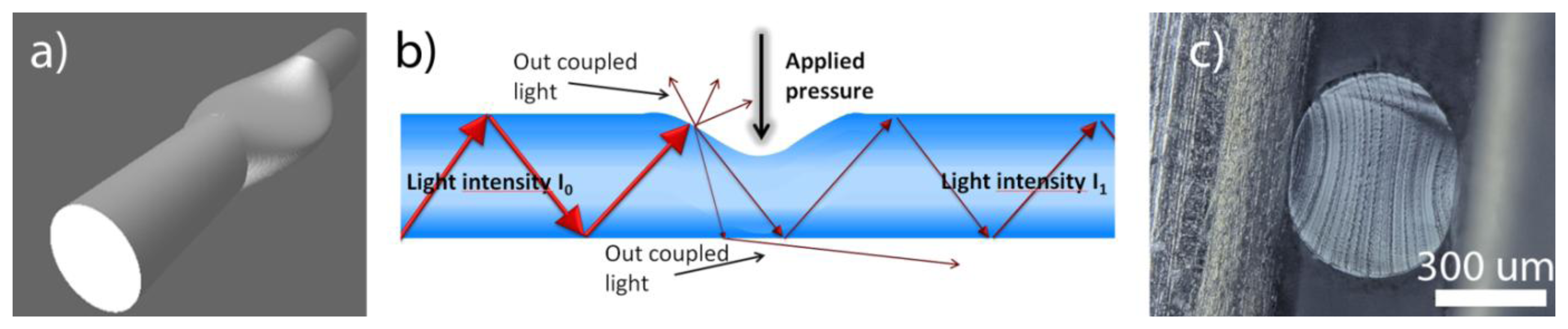
In hot places, air near the ground is hotter thanĪir at a height. That light entering the diamond is total internally reflected from the many cutįaces before getting out as shown in Figure 6.22.
Larger range of angle of incidence (24.4° to 90° inside the diamond), to ensure A skilled diamond cutter makes use of this The critical angle of diamond is about 24.4°. Total internal reflection of light happens inside the diamond.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
